Key words: Graphite Electrodes, Refractory Material(brick, Mix), Copper Mould Tube, Mill Roll
+86 186 4091 3888
Key words: Graphite Electrodes, Refractory Material(brick, Mix), Copper Mould Tube, Mill Roll
+86 186 4091 3888
Dec. 16, 2021
A graphite electrode is nothing more than a sharp graphite rod, taken from a pile, subject to a support conductor for the current, a copper tube, and a plastic handle at a reasonable distance, a PVC pipe. The handle should be far enough away so that it does not soften it by overheating. In any case, it is clear that PVC is the worst plastic that can be used for this purpose, but it does exist.
This is the sheet metal welder for almost any metal. It requires no input material and actually does not allow it unless they are very fine rods. This has nothing to do with arc welding. It is the graphite tip that melts the metal, and it quickly turns bright white. The current heats the graphite, not the metal, graphite electrode, because the first has greater resistance and dissipates most of the power. The sharpness of the graphite tip is important for two reasons.
The thinner the contact point between the material and the tip, the greater the resistance to current and the greater the temperature range. If it is too thick, heat is easily transferred from the tip to the iron, and most of the heat dissipates without reaching the necessary temperature. The soldering iron will only work if it concentrates most of its power on the point to be soldered. Everything must be considered for this.
The fact that it was done in 10 minutes with no other ideas is quite good. The grip of the graphite electrode is a friend's idea and it is interesting in its simplicity. It involves making two cuts at the edge of the tube, dividing it longitudinally into 4 more or less equal parts. Two of them are eliminated, leaving two tabs on the tube. Each one is tightened with pliers so that it is round and then fits into the bar and then close to each other. You are looking for a large brass nut that snaps into place and has no bar; you turn the nut hard enough to make a thread in the brass. Then open it up, put the bar in and do the same thing that is perfect for the subject. This system allows for quick bar changes, adjustment of their position and provides good electrical contact.
Super High Power Graphite Electrode
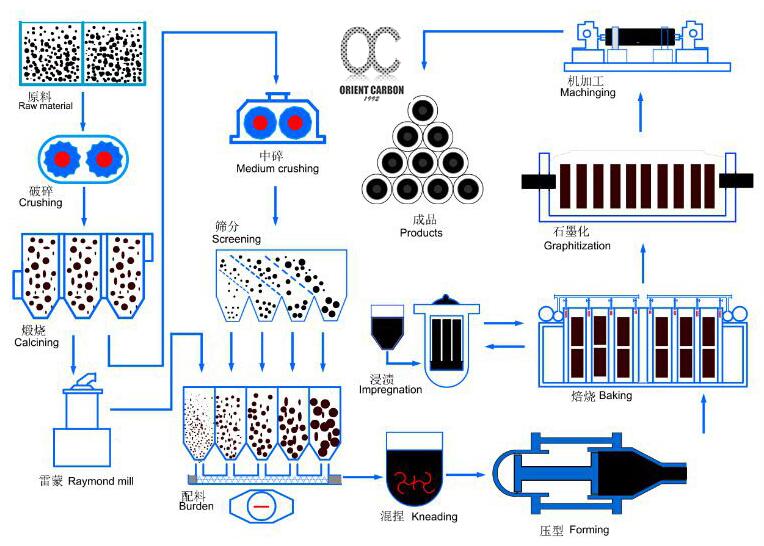
1. Raw material: high quality calcined petroleum coke and needle coke are used
2. Calcination: The raw material containing carbon is heat treated at 1250-1350℃ to discharge the contained moisture and volatile fraction and improve the production of raw material performance accordingly.
3. Crushing, sieving and batching: Before batching, large calcined petroleum coke and needle coke are crushed, ground and sieved, and then processed into various sizes of aggregates and powders according to the formula requirements. , Binder is calculated separately and weighed according to the composition.
4. Mixing and kneading: At a certain temperature, the process of synthesizing the plastic paste by mixing the quantitative carbonaceous particles and powder of various particle sizes with the quantitative coal pitch and stirring them well.
5. Forming: The mixed carbon paste is plasticized and deformed under the external force of the forming equipment to form a raw billet with certain shape, size, density and strength.

6. Roasting: is under the protection of filler, in the carefully designed heating furnace for high-temperature heat treatment, so that the raw billet in the process of carbonization of coal pitch. The carbon products after calcination have higher mechanical strength, refractive index resistivity, better thermal stability and chemical stability.
7. Impregnation: The carbon material is injected into a pressure vessel with liquid asphalt cement under certain temperature and pressure conditions to reduce the porosity of the product, increase the bulk and mechanical strength of the product, and improve the conductivity and thermal conductivity of the product. Products.
8. Second baking: The production of electrodes with high bulk density requirements (except RP) and joint blanks need second baking, and joint blanks need three dipping and four baking or two dipping and three baking.
9. Graphitization: The purpose of graphitization is to improve the electrical conductivity and torsion of graphite electrode, to improve the impact resistance and chemical stability of GE, to make GE with lubricity, wear resistance, to remove impurities and to improve the purity. Usually the graphitization temperature range of RP graphite electrode: 2500-2600 degrees, resistance range 8-11; the graphitization temperature range required for HP graphite electrode: 2600-2800 degrees, resistance range 6-8; the graphitization temperature range required for UHP graphite electrode: above 2800 degrees, resistance range 6 or less.
10. Machining: The purpose is to achieve the required size, shape, precision, etc., and to meet the requirements of the electrode body and joint use by cutting. Graphite electrode processing is divided into two independent processes, electrode body and joint.
11. Finished product and packaging inspection: The finished product inspection process includes appearance, weight, length, diameter, resistance, capacity inspection, etc.; packaging inspection is to check whether the label and mark are correct and whether the packaging is firm, etc. according to the customer's requirements.
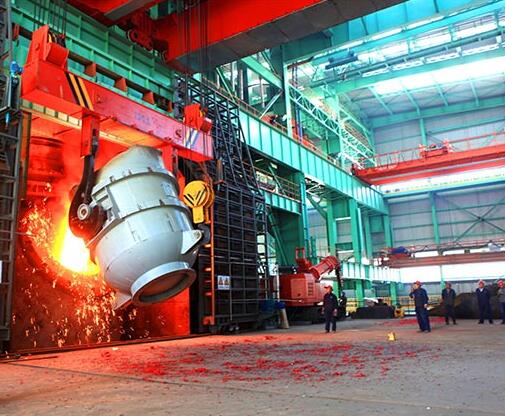
Graphite electrode is mainly used in electric arc furnace steel making. Graphite electrodes can provide a high level of electrical conductivity and the ability to withstand extremely high levels of heat generated. Graphite electrodes are also used in steel refining and similar smelting processes.
Graphite electrodes are mainly used in electric arc furnaces. They are currently the only products with high electrical conductivity and the ability to withstand the very high heat generated by EAF. Graphite electrodes are also used for refining steel in ladle furnaces and other smelting processes. There are four types of graphite electrodes: RP graphite electrodes, HP graphite electrodes, SHP graphite electrodes, and UHP graphite electrodes.
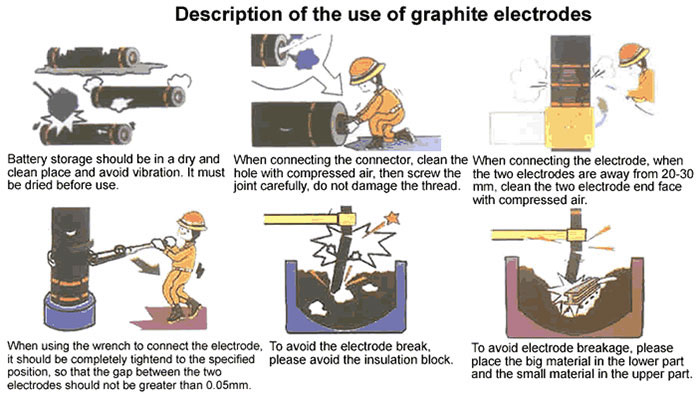
1. When connecting electrodes, if any threaded joint comes off, the threaded joint must be completed.
2. Identify the cause of the gap at the electrode connection and do not use until the gap is eliminated.
3. Application of electrode should avoid tilting operation, especially the connected electrode set cannot be placed horizontally to avoid breaking.
4、When charging into the furnace, the loose material should be loaded to the bottom of the furnace to minimize the influence of large furnace material on the electrode.
5. When melting, avoid stacking large pieces of insulating materials at the bottom of the electrode to avoid affecting the use of the electrode and even breakage.
6. Avoid collapsing the furnace cover when the electrode is rising or falling, so as not to damage the electrode.
7. Steel slag must be prevented from splashing onto the electrode threads or threaded joints stored at the smelting site and damaging the thread accuracy.
8. The electrode holder should be kept beyond the top electrode safety line; otherwise the electrode will break easily. The contact surface of the holder and electrode should be cleaned regularly to maintain good contact. The cooling jacket of the holder should avoid water leakage.
If you have any questions about graphite electrode, please feel free to contact our factory.
Navigation
Tel:: +86 186 4091 3888
Fax: +86 411 3962 5877
Mobile: +86 186 4091 3888
E-mail: jack@sncarbon.cn
Skype: graphite.sinometal@outlook.com
QQ: 695993847
Address: Zhongshan District, Dalian City,116001. China.